The aerospace industry is witnessing a transformative shift as 3D printed rocket engines gain traction. This innovative technology is poised to revolutionize the way rockets are designed, manufactured, and launched, promising a future where space exploration becomes more accessible and cost-effective.

3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has been steadily integrated into various industries, including aerospace. Companies like GE Aerospace have been using 3D printing since 2019 to produce components such as fuel nozzles and turbine blades for jet engines.[1] However, the application of 3D printing in rocket engines is a relatively new and exciting frontier.
3D printed rocket engines are created using techniques like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF). These processes involve precisely fusing layers of heat-resistant metal alloys or other advanced materials to build complex components or even entire 3D printed rocket engines.[3]
As the global race to innovate in 3D printing intensifies, China has positioned itself as a key player in this technological revolution, particularly in aerospace. With substantial investments in 3D printing research and development, Chinese companies and research institutions are pioneering advancements in materials and manufacturing processes that are critical for the development of 3D printed rocket engines. China's ability to produce high-quality, cost-effective components at scale is helping to drive down the costs of rocket engine production and accelerating the timelines for space missions. This strategic focus not only strengthens China’s position in the global aerospace market but also contributes to the broader adoption of 3D printed rocket engines worldwide.

1. Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printed rocket engines is their potential to drastically reduce manufacturing costs. Studies suggest that 3D printing can slash launch costs by up to 95% compared to traditional methods.[2] Companies like Relativity Space and Launcher are leveraging this cost-effective approach, making space exploration more accessible to various stakeholders.
2. Speed of Production
3D printing enables accelerated development and production timelines for rocket engines. For instance, Ursa Major, a startup specializing in 3D printed rocket engines, has been able to move from years to months in engine development.[2] This rapid prototyping capability allows for iterative improvements and faster time-to-market.
3. Design Flexibility
Traditional manufacturing methods often impose limitations on the complexity of designs for rocket engines. 3D printing, however, opens up new possibilities for optimized and intricate designs that were previously impossible or prohibitively expensive. GE Aerospace has utilized 3D printing to create complex components like fuel nozzles and turbine blades[1], while Relativity Space's Terran 1 rocket showcased the potential for reducing the number of parts from thousands to just a few.[3]
4. Material Efficiency
Additive manufacturing processes minimize material waste by building components layer by layer, utilizing only the required amount of material for 3D printed rocket engines. This not only reduces costs but also allows for the use of advanced materials like heat-resistant metal alloys, which can enhance the performance and durability of rocket engines.[3]
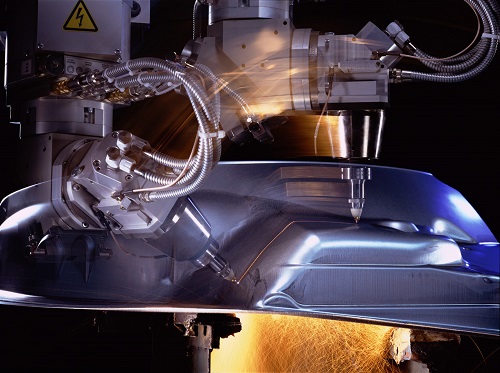
As the world of 3D printing continues to evolve, events like TCT Asia serve as platforms for showcasing the latest innovations and advancements in additive manufacturing technologies, including 3D printed rocket engines. TCT Asia is a leading event focused on 3D printing, attracting industry leaders, researchers, and enthusiasts from around the globe.
By attending TCT Asia, you can gain firsthand insights into the cutting-edge developments in 3D printed rocket engines and other applications of additive manufacturing. This event provides an opportunity to network with experts, explore the latest products and services related to 3D printing in aerospace, and stay ahead of the curve in this rapidly evolving field.
The rise of 3D printed rocket engines is a testament to the transformative power of additive manufacturing. With their cost efficiency, accelerated production timelines, design flexibility, and material efficiency, 3D printed rocket engines are poised to disrupt the aerospace industry and make space exploration more accessible than ever before.
As industry leaders like Relativity Space, Ursa Major, and GE Aerospace continue to push the boundaries of what's possible with 3D printed rocket engines, it's an exciting time to follow the latest developments in this field. By attending events like TCT Asia, you can stay informed and witness firsthand the innovations that are shaping the future of space exploration and beyond.
[1] GE Aerospace to scale the production 3D printed jet engines with $650 million investment. 3D Printing Industry. Available at: https://3dprintingindustry.com/news/ge-aerospace-to-scale-the-production-3d-printed-jet-engines-with-650-million-investment-228977/ (Accessed: [current date])
[2] Relativity Space website. Available at: https://www.relativityspace.com (Accessed: [current date])
[3] Buchanan, C. and Knibbs, N., 2022. 3D printed rocket engines: the technology driving the private sector space race. The Conversation. Available at: https://theconversation.com/3d-printed-rocket-engines-the-technology-driving-the-private-sector-space-race-168146 (Accessed: [current date])